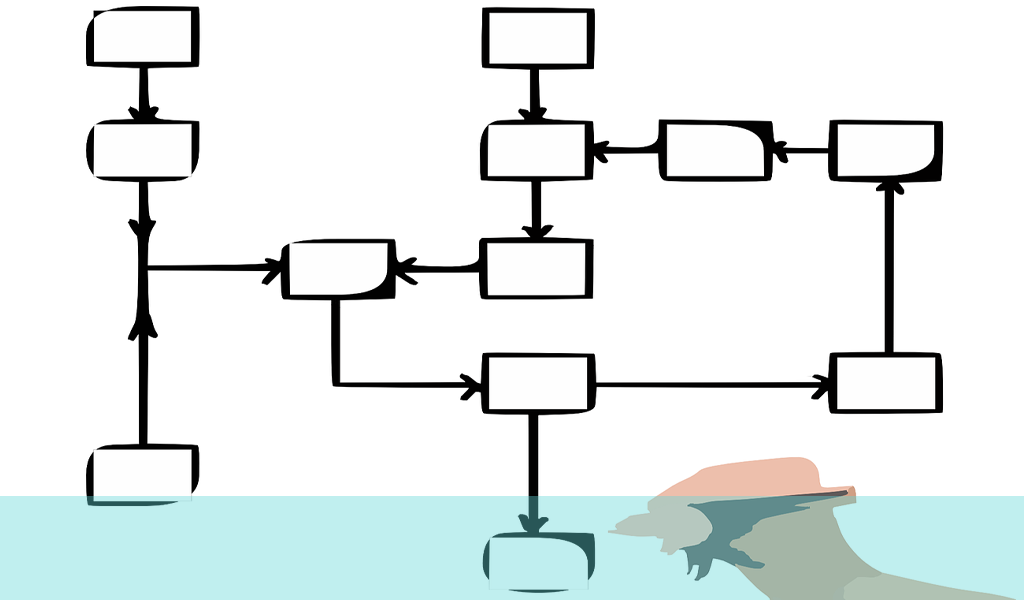
A customer journey map will feature a number of useful and critical elements in order to perform its function in an optimum way. Most of these elements will focus on some characteristic of the user;
- The first thing to determine is whose journey are we mapping and where they are going/what they are trying to achieve – this could be customers but it might also be suppliers, VIPs, influencers, media, contractors, in fact anyone who might interact with you and your organisation in any business-related context;
- This will include understanding their needs, motivations, beliefs, interests, actions etc (these traits will have been defined if you have produced online personas for users);
- The scope of the customer journey should be clearly identified and articulated so there is absolute clarity on what is being examined;
- Where the user touches the organisation during their journey and the channels they use are also important factors;
- The current or potential beartraps in the system should be highlighted and their ability to derail customer journeys (or at least severely disrupt the journey or irritate the user) should be analysed and assessed;
The most important feature in preparing a customer journey map is understanding the customer and the only way to achieve this is through research. This can take several forms:
Existing Data
There will be a wealth of data already in existence in your organisation – customer records, sales records, website analytics and other information gathered from website visits, previous research commissioned into user characteristics, attitudes etc, information gathered from promotions etc. Take a look around and talk to people in your organisation to find out what has been done and where useful information might be lurking;
Anecdotal Information
There could also be a lot of qualitative or anecdotal data around your business eg salespeople’s interface with customers might throw up concerns, likes and dislikes, motivations and reasons for purchase or non-purchase that could be beneficial in constructing user profiles. Receptionists and call centre or phone-based staff might also have key information in these areas and web designers might provide insights into user behaviour, navigation routes, page popularity, conversion rates and other indicative data and, finally. Social media tracking can provide insights into what consumers like and dislike about your products, business, website
Commissioned Research
You can also commission research yourself. This could be quantitative or qualitative research – in other words it can produce usable figures with little descriptive enhancement or it can be more narrative, detail-rich research providing deeper insight and understanding of attitudes, desires, motivations and so on.
Whatever methods you decide to use it is important that it focuses in on user characteristics and behaviour. If you would like to know more about customer journey mapping and how to go about researching for them, why not ring us on +44(0)800 0246247 or email us at hello@ux247.com
















It’s in point of fact a nice and helpful piece oof information. I am happy that you simply
shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this.
Thank you ffor sharing.
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am in fact impressed tto read everthing aat alone place.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after
browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me.
Nonetheless, I’m definitely glad I fouund itt and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
Hello, I read your blog daily. Your humoristic style is awesome, keep it up!